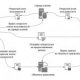
Data Storage Facility

Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory, English flash memory), high access speed and rapid data washing
Energy dependency
(angl. nonvolatile storage) - ZU, which records do not erase when electricity is removed. This type of memory includes all types of ELVs and IPFs.
Energo-dependent memory (waste storage) - ZU, which is erased when electricity is removed. This type of memory belongs to the OSS, the kash-pm.
( dynamic storage) - the variety of energy-dependent semi-conductor memory, in which the stored information has been destroyed over time, so periodic remediation (regeneration) is required to preserve the records, which is managed by special external schematic elements.
static storage) is the variety of energy-dependent semiconductor memorial that is sufficient to store information to maintain the energy supply voltage and no regeneration is required.
By type of physical host and principle of rEMA
Some memorials may carry two or more “people” names on the principle of work.
Acoustic memory (angl acoustic storage) - closed acoustic delay lines are used as an environment for recording and storing data.
Geographical memory (angl. holographic storage) - Spatial graphics are used as an environment for recording and storage as displayed in the form of interpretation structures.
Ambient memory (angl. capacitor storage) is the type of RU used as an environment for recording and data storage elements The electrical circuit is capacitors.
Cryogenic storage (angl. cryogenic storage) - Superconductive material is used as an environment for recording and storing data.
Laser memory (angl. laser storage) is a memory in which the data are recorded and readable by a laser (CD-R/RW, DVD+R/RW, DVD-RAM).
Magnetic memory (angl. magnetic storage) is a memory that uses magnetic material as an environment for recording and storing data. The most widely used magnetic remembrance devices in modern computers are magnetic tape recorders (NMLs), magnetic disk (high and flexible) disk (HMM and NGM). Some varieties have their own names: